Organic Chemistry Online
Stereochemistry
Stereochemistry is the study of the three-dimensional spatial orientation of molecules i.e. stereoisomerism. The chart below and the examples that follow depict isomerism in general.
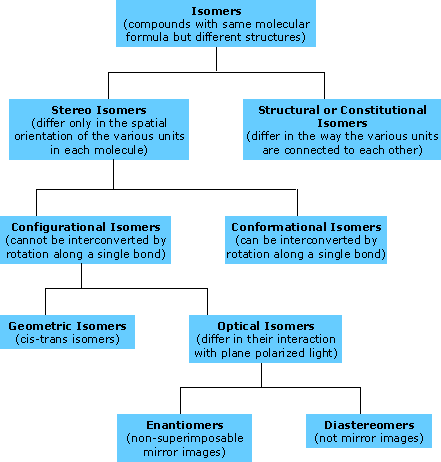
Examples:
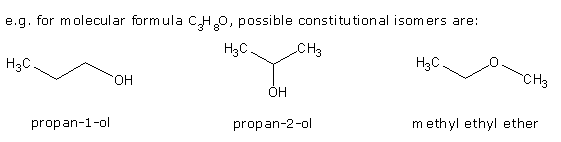
1. Structural or constitutional isomers: same molecular formula
but differ in the way the various groups
are connected to each other.
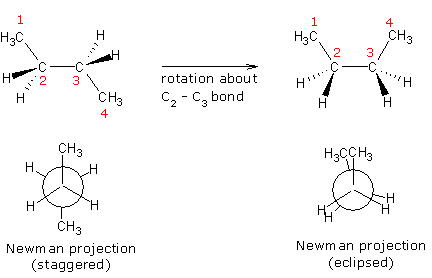
2. Conformational isomers: stereoisomers that differ
only by rotation along single bonds.
3. Geometric (cis-trans) isomers: stereoisomers that differ in
configuration about a C-C double bond or
cyclic structure, e.g. for 2-butene:
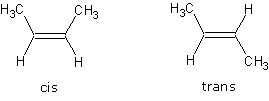
Features | Glossary | Quiz